Discuss your challenges with our solutions experts
How are olefins made from CTO/MTO?
Kelly Cui, Olefins Senior Consultant, gives an overview of the coal-to-olefins/methanol-to-olefins process and the technologies supporting it.
1 minute read
Kelly Cui
Principal Analyst, Petrochemicals

Kelly Cui
Principal Analyst, Petrochemicals
Kelly is an expert in the coal-to-olefins (CTO) and methanol-to-olefins (MTO) sector.
Latest articles by Kelly
-
The Edge
Big Oil’s opportunity for M&A in the petrochemicals downturn
-
Opinion
Why crude-to-chemicals is the obvious way forward
-
Opinion
Coronavirus to disrupt China’s chemicals sector more than SARS
-
Editorial
Why is China the early adopter of CTO/MTO
-
Editorial
The opportunities and challenges of CTO/MTO development
-
Editorial
How are olefins made from CTO/MTO?
The process
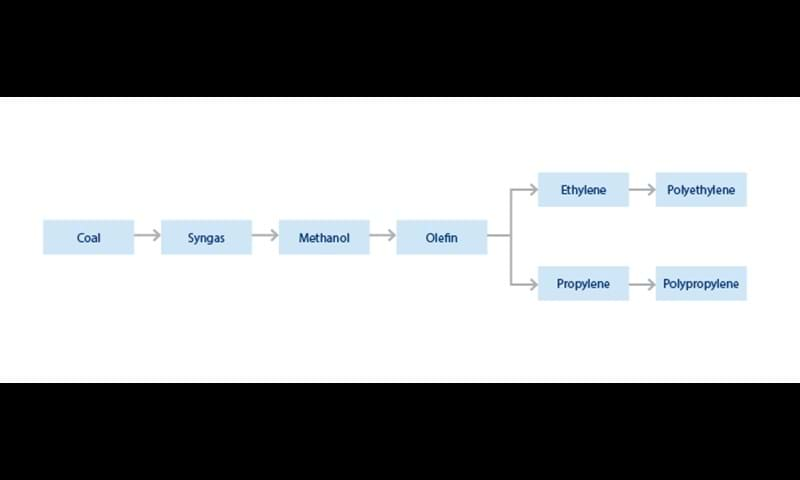
Methanol is an intermediate for the coal-to-olefins (CTO) process and a direct feedstock for the methanol-to-olefins (MTO) process. To produce the methanol intermediate for the CTO process, coal gasification produces syngas (carbon monoxide), which is then converted to methanol by traditional technologies.
Both MTO and methanol-to-propylene (MTP) technologies use specialized catalysts to promote the conversion of methanol into olefins. Put simply, MTO technology uses a fluidized bed reactor to convert methanol into ethylene, propylene and water, while MTP technology uses an initial reactor to convert methanol into dimethyl ether (DME), and then parallel fixed bed reactors to convert DME into propylene, gasoline and water.
The technology
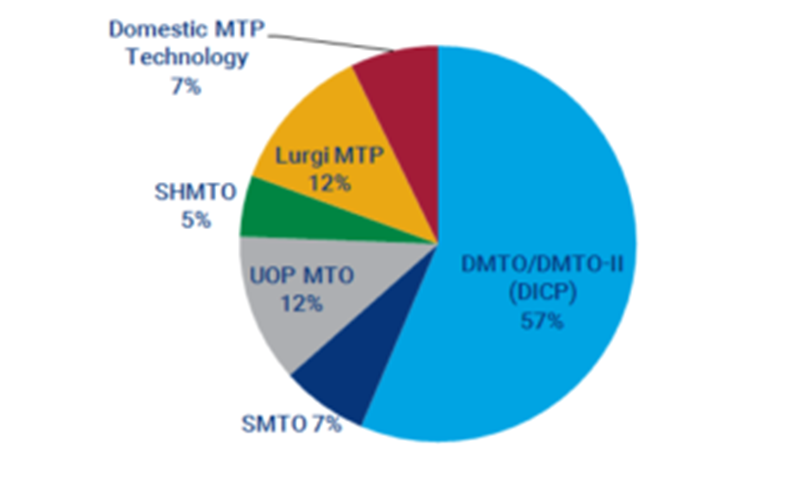
DMTO, as the first MTO technology used in China, is the most common type of technology among existing plants, accounting for 57% of total coal- and methanol-based olefins. The majority of DMTO-I (and DMTO-II) technology users are state-owned companies such as Shenhua and China Coal group. Tied for second place with 12% of market share each, UOP's MTO technology has been well received by private companies, while Lurgi's MTP technology is mainly used by Shenhua and Inner Mongolia Datang.
Other potential technologies
Like other industries, technological development and innovation is crucial to improved CTO/MTO efficiencies, yields, and ultimately the cost of olefins production. Two potential technologies are on the horizon, including DMTO-III and a syngas-to-olefins technology, which would skip over methanol synthesis.